3D Printers 102
You really want to know how each part works, if not good luck fixing your printer.
Parts of a 3d Printer
Recap. You should have been paying attention to 3d printers 101 :(
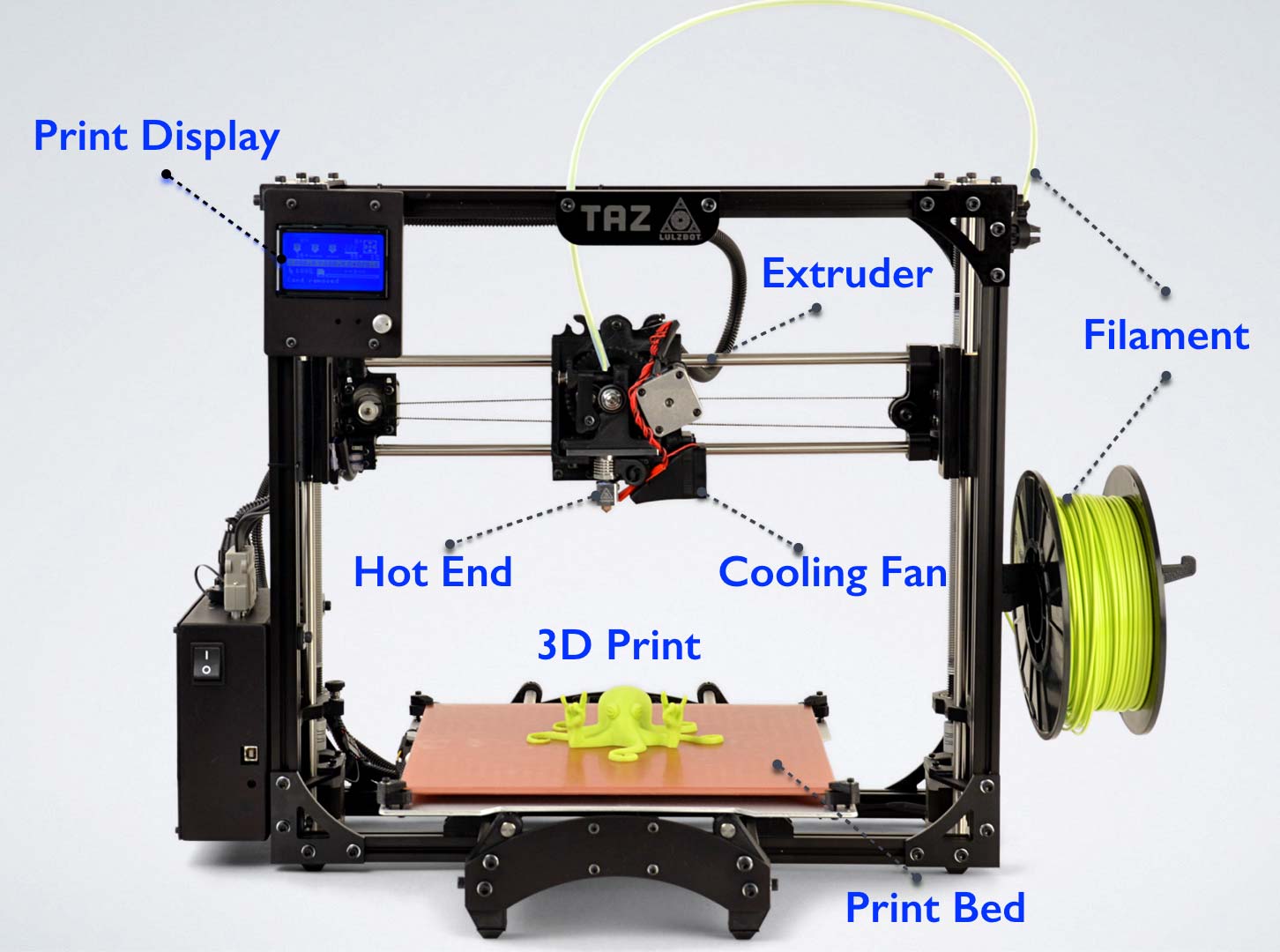
Source: http://my3dconcepts.com/explore/main-components-of-desktop-3d-printers/
Nozzle (found attatched to your hotend)
Nozzle Size
Nozzle diameters affect many aspects of your print, from precision to speed. The goal is to balance speed and precision in your prints.
Larger Nozzles (>0.4mm)
- Faster print time
- Fewer maintainance/nozzle-related errors
Smaller Nozzles (<0.4mm)
- High Precision
- More maintainance (clogging)
Commonly, most people use 0.4mm nozzles as it has a good balance between speed and precision. As such, it is commonly recommended to go for 0.4mm nozzles.
Hot end

The hotend melts the filament into thin lines for printing. The quality and type of the hotend affects the chances of failed prints and the print quality. Hotends also affect the types of materials you can print with as different hotends support different temperature heating. Generally, all-metal hotends are more expensive, offer higher temperatures and overall better quality compraed to standard hotends.
Cooling (Part cooling fans)
Part cooling fans cools the hot freshly extruded plastic as soon as it exits the nozzle. This eliminates various forms of print problems. However, there are several materials such as ABS that will create more problems with a part cooling fan on. As such, it is recommended to always check if a part cooling fan is needed for different materials. For most filaments such as PLA, a part cooling fan is recommended.
FYI: our school uses PLA mostly, so ensure the part cooling fan is on and working.
Print Bed
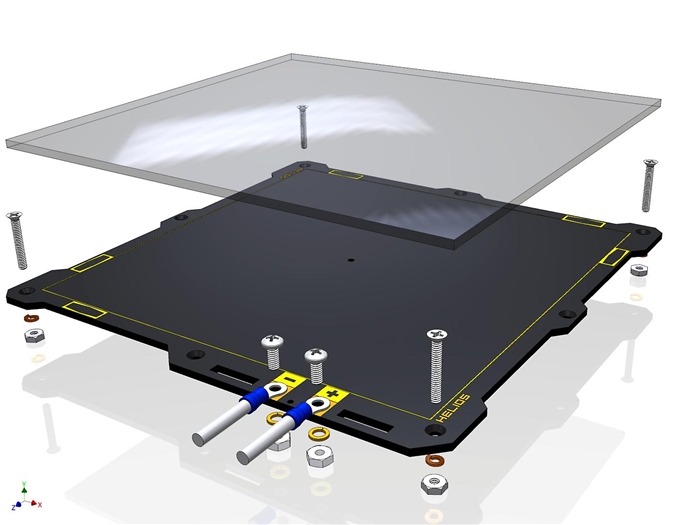
Heated beds
Heats up the bed.
- More stable prints / Better bed adhesion
- Reduced warping (warping occurs due to uneven cooling at the edges comapred to the interior. A heated bed prevents that)
- Allows you to print different types of materials
Non-heated Beds
Basically non heated…
So…
Heated beds are helpful but not always necessary. Different materials require different temperature and sometimes heated beds. However, high print quality can still be achieved with a heated bed.
Direct Drive extrusion vs Bowden extrusion
Direct extrusion:
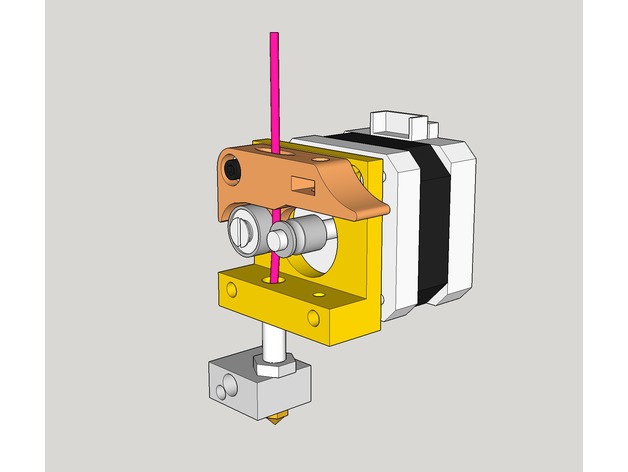
Basically, filament enters the nozzle directly
Pros:
- Better extrusion (the motor can easily push filament through the nozzle)
- Faster retraction (Because the extruder is literally next to the nozzle, it can retract filament better)
- Wide range of materials that can be printed (It works for lots and lots of filaments)
Cons: Since there is an increased weight from the extruder and its motor, the additional weight can result in backlash, banding, overshoot or frame wobble. Basically, increased weight, so you get more wobble and problems with your movement. And this results in a possible loss of accuracy.
Bowden Extrusion:

Filament is pushed through the PTFE tubing by the extruder before reaching the hotend/nozzle.
Pros:
- Lighter (Less weight, faster and no more direct extrusion problems)
- Faster print (lighter weight results in faster movements and thus faster prints at high speeds)
Cons:
- Slow response times due to more friction within the PTFE tubing. Bowden extruders also require longer and faster retraction compared to direct extrusion.
- Less materials that can be printed. (Flexible filaments and abrasive filaments dont really like PTFE tubing and causes binding)
So which one then?
Its more of what do you need…
- Do you want speed, precision and standard materials? Go for bowden extrusion.
- Do you want a wider range of materials to print from? Go for direct extrusion
FYI: our school uses bowden extrusion, because we dont print with flexible filaments and mostly for its speed.